low end tidal co2 during cpr
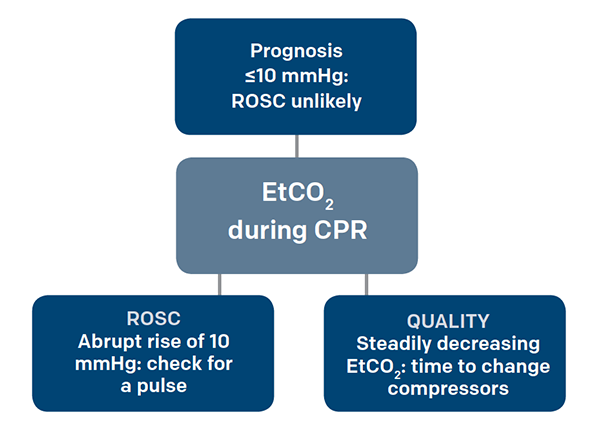
End-tidal CO2 ETCO2 detection requires air movement. Goal is 10 mmHg during CPR.

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News
Affordable CPRAED Online Training Available.

. Prognostic value of end-tidal carbon dioxide pressures during out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. End tidal carbon dioxide ETCO 2 monitoring is the noninvasive measurement of exhaled CO 2 first studied clinically by Smallhout and Kalenda in the 1970s. A study was undertaken to determine the pattern of end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 changes during asphyxia-induced cardiac arrest in a pediatric canine model.
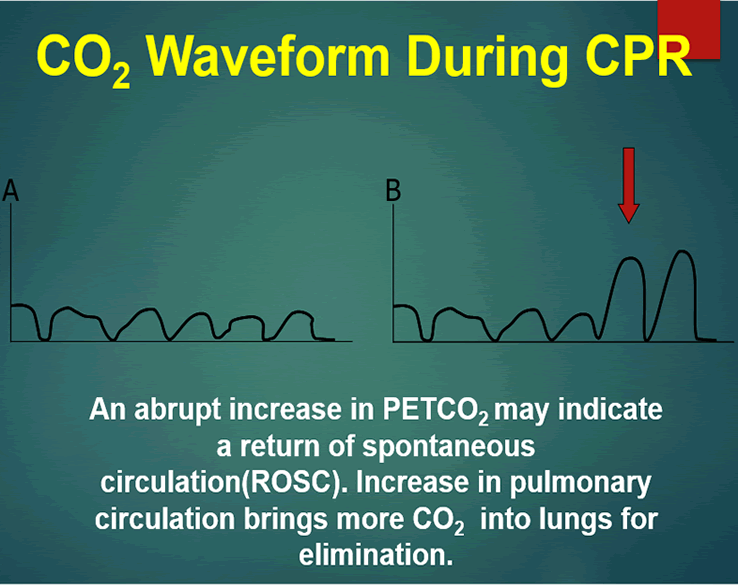
Abrupt increase in ETCO2 suggests ROSC during CPR detectable before pulse check ETCO2 at 20 minutes of CPR is prognostically useful. Ad Money Back Guarantee Register Now. Measurement of a low ETCO 2 value 10 mmHg during CPR in an intubated patient suggests that the quality of chest compressions needs improvement.
Mean weight 55 kg were used. On the other hand a high CO2 reading may indicate airway narrowing. In fact its commonly called the ventilation vital sign.
N Engl J Med 1988318607-11. During CPR ETCO2 levels were initially high decreased to low levels. Free Wallet Card in Mail Group Discounts Available CPR Healthcare Online Course.
Eleven intubated anesthetized paralyzed dogs mean age 41 mo. Murphy RA Bobrow BJ Spaite DW et al. E tco 2 During CPR.
1 that etCO 2 can distinguish massive PE from hemorrhagic shock and 2 that PE with cardiac arrest reduces etCO 2 during resuscitation to a greater extent than arrhythmic cardiac arrest. End-tidal carbon dioxide and outcome of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. On the other hand a high CO2 reading may indicate airway narrowing.
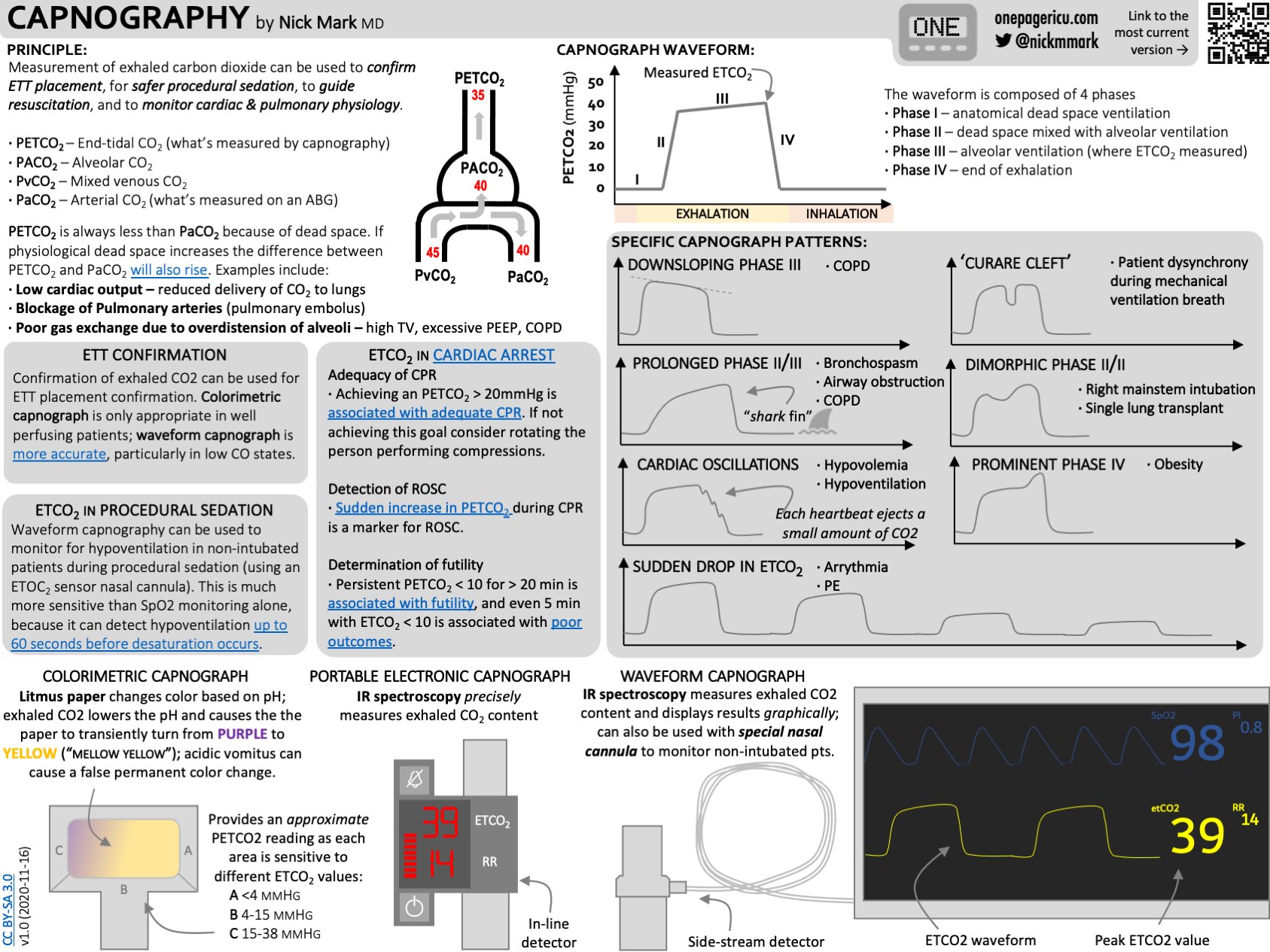
More Than Just a Number. End-tidal carbon dioxide ETco 2 monitoring provides valuable information about CO 2 production and clearance ventilation. The goals of this review are to confirm and quantify this.
End-tidal carbon dioxide concentration during cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Ad Full Refund If Your Card Is Not Accepted By Employer. Also called capnometry or capnography this noninvasive technique provides a breath-by-breath analysis and a continuous recording of ventilatory status.
39 Treveno RP Bisera J Weil MH Rackow EC Grundler WG. Crit Care Med 198513910-11. Levine RL Wayne MA Miller CC.
Get Certified In FA CPR AED. Cardiac output and end-tidal carbon dioxide. 5 In low-flow states such as during CPR delivery of CO 2 to.
A low end-tidal CO2 may indicate poor perfusion hypovolemia or sepsis. N Engl J Med. Falk JL Rackow EC Weil MH.
In ideal conditions CPR can achieve as much as 25 of normal cardiac output converting the no-flow state of cardiac arrest to a low-flow state Bellamy et al. CPR is a low cardiac output state during which E tco 2 becomes less dependent on CO 2 production and ventilation and more linearly related to cardiac output. Loss of ETCO2 may be the first sign that CPR is needed.
Ann Emerg Med 0 by Asplin BR. End-tidal CO2 as a guide to successful cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Changes in expired endtidal carbon dioxide during cardiopulmonary resuscitation in dogs.
End-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO 2 as measured by waveform capnography is considered a physiologic measure of cardiac output in low-flow states and has been proposed in the 2010 consensus resuscitation guidelines as a possible real-time metric to assess the impact of CPR quality. We investigated the effect of massive pulmonary embolism MPE on end tidal CO 2 etCO 2 and tested two hypotheses. Measurements during cardiopulmonary resuscitation CPR reflect variable cardiac output over time and low values have been associated with decreased survival.
A prognostic guide for resuscitation efforts. Ad Hands-On Flexible Classes In Locations Near You. Get Certified And Help Save A Life.
Online CPR Certification for Workplace Healthcare Providers. Free Full Text Critical Care. J Am Coll Cardiol.
Although the normal range for CO2 should be between 35-45mmHg CO2 monitoring gives healthcare providers a lot more insight into what is going on with a patients condition. Here are five things you should know about waveform capnography in cardiac arrest. Normal ETCO2 in the adult patient should be 35-45 mmHg.
Use End Tidal Capnography For Placing Orogastric Nasogastric Tubes And Cpr Page 2 Of 4 Acep Now Page 2

The Role Of Etco2 In Termination Of Resuscitation Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

Emergency Intubations Capnography

Capnography During Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Current Evidence And Future Directions

Reversible Causes Of Low Etco2 In Cpr Criticalcarenow

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
Nick Mark Md On Twitter End Tidal Co2 Monitoring Capnography Is An Important Technique To Guide Resuscitation Confirm Ett Intubation Monitor Physiology Amp Make Procedural Sedation Safer Here S A New1 Onepager All About

The Impact Of Ventilation Rate On End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Level During Manual Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Resuscitation

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationcapnography In The Ed Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi
Cpr Mobile Code Stand With Capnograph Capnography

Quantitative Waveform Capnography Acls Medical Training

Average Etco2 Kpa During Cpr In Patients With Or Without Rosc Download Scientific Diagram
